Installing Jetty on Ubuntu
So lets say you are trying to set up some certificates in a Java keystore on a server and you are hitting a brick wall. You might want to quickly set up a test environment to test your certificates and keystore in isolation. Here are some quick instructions on how to set up a server for testing. These are all based on installing Jetty 9.4.45-1 on Ubuntu 22.04. YMMV with other versions.
Before installing Jetty it’s a good idea to run the following three commands first to make sure your Ubuntu install has all its relevant patches…
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo reboot
Installing Jekyll
Run the following command which installs Jetty and its dependencies…
sudo apt install jetty9
Starting Jetty using systemctl
The following will tell the operating system that you want Jetty to start at boot…
sudo systemctl enable jetty9
And this will start the Jetty service…
sudo systemctl start jetty9
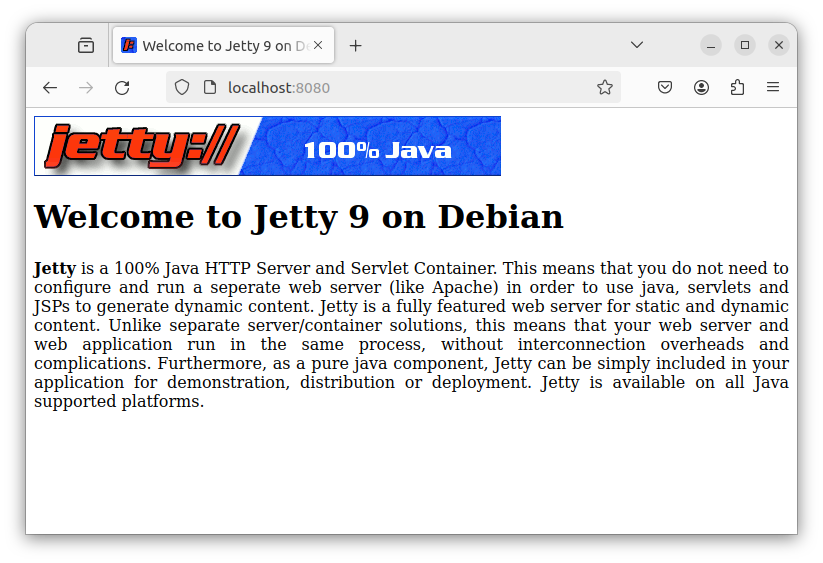
At this point you should be able to open a web browser and visit http://localhost:8080/ to see your Jetty install running.
To stop the service you can run the following…
sudo systemctl stop jetty9
Starting Jetty from the command line
The following command will start Jetty using the same parameters and configuration files used by systemctl…
sudo /usr/bin/java -Djetty.home=/usr/share/jetty9 -Djetty.base=/usr/share/jetty9 -Djava.io.tmpdir=/tmp -jar /usr/share/jetty9/start.jar jetty.state=/var/lib/jetty9/jetty.state jetty-started.xml
Configuring HTTPS
Make sure that Jetty isn’t running first.
Run the following command to add the HTTPS and SSL modules…
sudo /usr/bin/java -Djetty.home=/usr/share/jetty9 -Djetty.base=/usr/share/jetty9 -Djava.io.tmpdir=/tmp -jar /usr/share/jetty9/start.jar --add-to-start=ssl,https
At this point you should be able to visit https://localhost:8443 and see your Jetty install using HTTPS. However it will be using a self-signed certificate so the web browser will likely give you a warning about the connection not being secure.
If you have your own Java keystore file with valid signed certificates you can drop it in the /etc/jetty9/ folder where Jetty expects to find it. And then update the following lines in /etc/jetty9/start.d/ssl.ini to point to the new keystore, and to give it the password that will allow it to access the certificates in the keystore.
## KeyStore file path (relative to $jetty.base)
jetty.sslContext.keyStorePath=etc/keystore.jks
## TrustStore file path (relative to $jetty.base)
jetty.sslContext.trustStorePath=etc/keystore.jks
## KeyStore password
jetty.sslContext.keyStorePassword=MYSECUREPASSWORD
## KeyManager password
jetty.sslContext.keyManagerPassword=MYSECUREPASSWORD
## TrustStore password
jetty.sslContext.trustStorePassword=MYSECUREPASSWORD
If you start Jetty now using the systemctl command or the /usr/bin/java command it should successfully read from the certificates in your keystore and allow people to connect securely.